DB2 PureScale Startup Failure
1. Issue Description
The DB2 PureScale database in the client’s core marketing system experienced a sudden failure and was unable to restart after crashing.
- Hardware Resources: CPU 40 Cores / MEM 128GB
- Operating System: RedHat 7.5
- DB2 Version: DB2 v11.1.4.5
2. Problem Analysis
The engineer determined that the database cluster had unexpectedly stopped, with the error message:
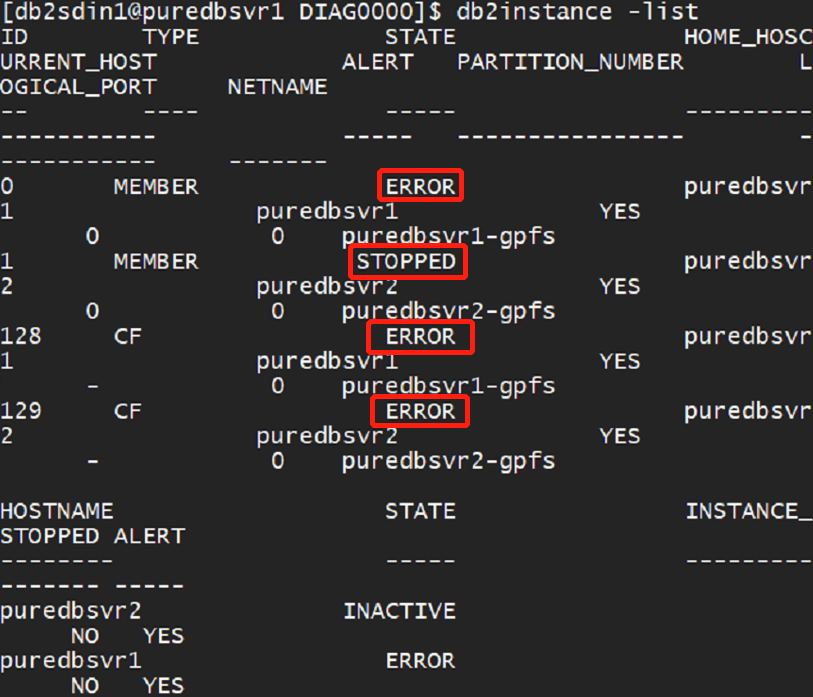
"Node unable to establish a session with the cluster manager."
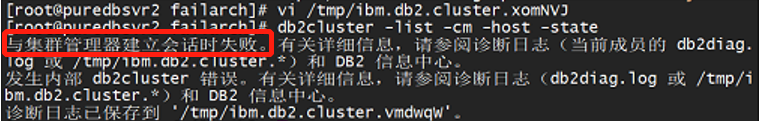
The database log showed a "Repair Domain failed" error, indicating that an attempt to repair the cluster was unsuccessful. Manual restart attempts for the database also failed.
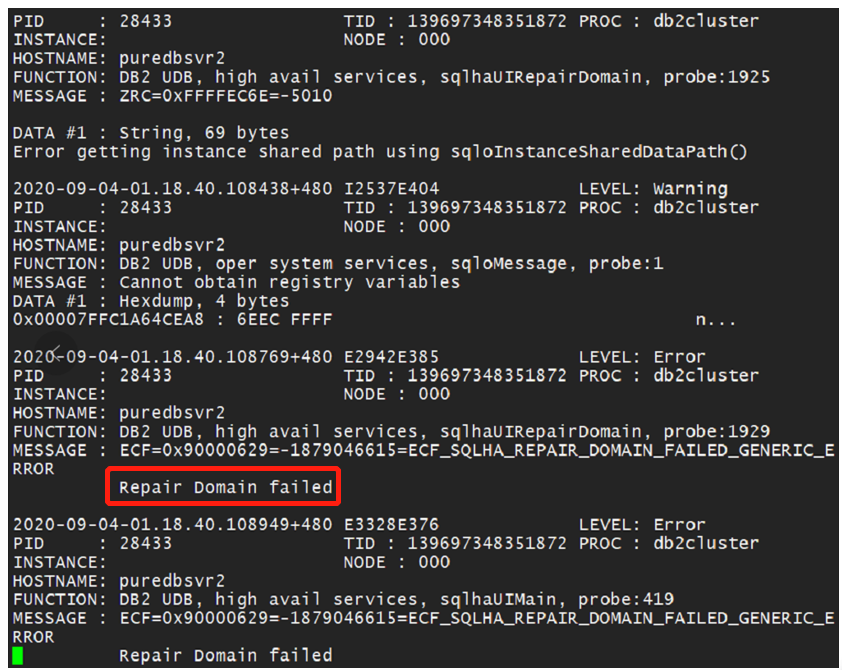
Reviewing the GPFS logs revealed errors indicating the GPFS file system was not able to prepare properly, resulting in a failure to mount the GPFS file system on both nodes.
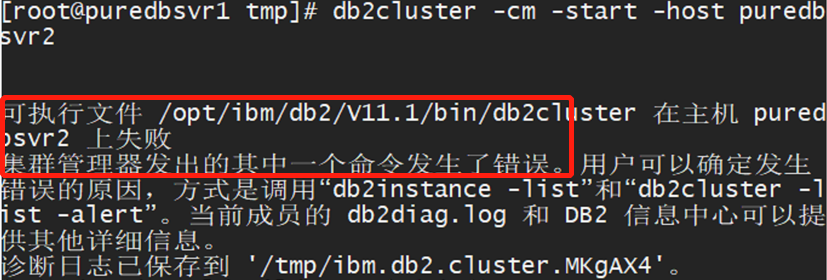
Since DB2 PureScale relies on GPFS as its shared file system, a GPFS failure renders the DB2 database unusable.
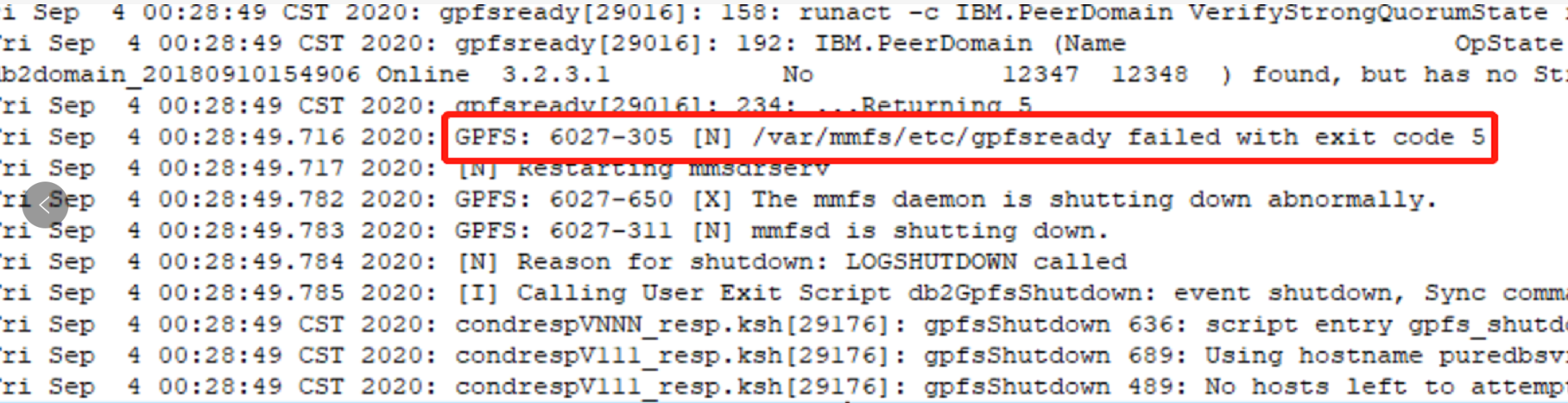
3. Problem Resolution
To address the GPFS 6027-305 issue, the engineer consulted the official guide, modified the verifyGpfsReady setting to “no,” and disabled the verifyGpfsReady feature. This resolved the issue with /var/mmfs/etc/gpfsready not executing successfully. After applying this fix, GPFS started normally, and the file system was able to auto-mount. The DB2 PureScale cluster service comprises three main components:
- Cluster Manager: Tivoli SA MP, featuring Reliable Scalable Cluster Technology (RSCT)
- Shared Clustered File System: IBM General Parallel File System (GPFS)
- DB2 Cluster Management: Manages and monitors the cluster with DB2 commands and views
Once the GPFS issue was resolved, RSCT commands like lsrpdomain and lsrpnode were operable on one node. However, attempts to run these commands on the second node returned error 2612-022.
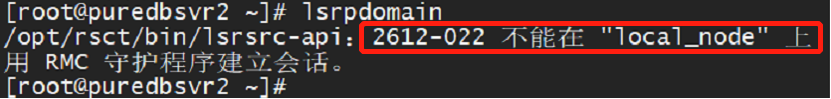
This error indicated that the RSCT resource group had not started properly, preventing access to the configuration resource manager. 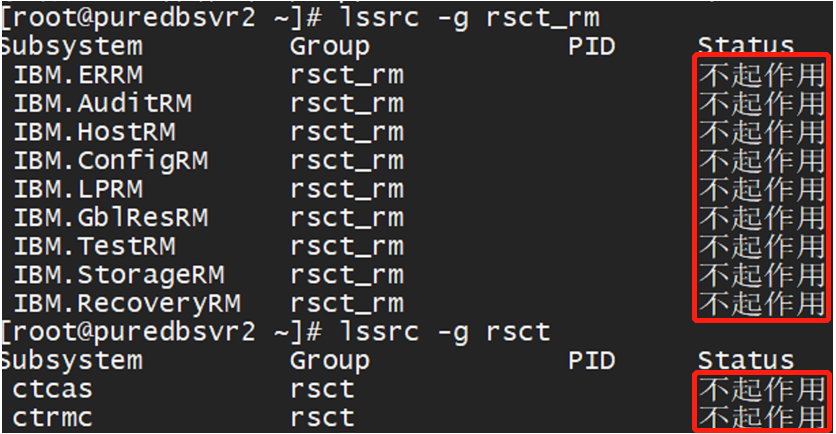

To resolve this, steps were taken to re-establish the remote client connection between the two nodes:
bash/usr/sbin/rsct/bin/rmcctrl -A
/usr/sbin/rsct/bin/rmcctrl -pAfter these steps, the database was able to start successfully.

4. Summary of Lessons Learned
- When troubleshooting similar issues, it is critical to analyze DB2, GPFS, and RSCT logs sequentially to accurately identify the root cause.
- Communication with the client revealed that an OpenSSH upgrade had been performed on the same day. The engineer concluded that this upgrade led to a trust issue between the two DB2 cluster nodes.
- Maintenance personnel should inform all relevant parties (system administrators, database administrators, and application maintenance staff) of any system changes to prepare for and mitigate unexpected failures.